signs of disease
- Urination disorder, characterized by an intermittent, weak, and abnormally short flow of urine that causes splashing, difficulty, and pain before urinating. Frequent urges to empty your bladder occur mostly at night.
- The pain is localized in the lower abdomen and radiates to the scrotum, perineum, and rectum.
- Sexual dysfunction.
- Ejaculation problems, sperm changes (consistency, quantity).
acute prostatitis
- Seminal vesiculitis is inflammation of the seminal vesicles and is responsible for the presence of pus in sperm, which not only reduces the quality of ejaculation but also leads to loss of reproductive function.
- Colonitis - inflammatory changes in the spermatozoa become the cause of severe pain during sexual intercourse, interrupted orgasm and psychogenic impotence.
- The formation and rupture of abscesses in the prostate and purulent lesions of the rectum can lead to worsening of symptoms, severe physical intoxication, and even death.
- Stagnation of prostate tissue causes changes in its structure, disrupting the innervation and blood supply of the gland itself and nearby organs, thereby disrupting its function. Erection is insufficient for adequate sexual intercourse, premature ejaculation and prolonged intercourse without orgasm are observed.
- Scarring changes to the glands and spermatic cord can lead to infertility, decreased sperm quality and sperm motility. Narrowing of the urethra can interfere with the normal urination process; bladder obstruction can lead to acute urinary retention, requiring emergency surgery.
chronic prostatitis
- fever;
- Pain occurs in the scrotum, perineum, anus, and back;
- Urination disorders;
- Mucus or mucopurulent discharge from the rectum or urethra even without urination or defecation;
- Erectile dysfunction, painful ejaculation, interrupted intercourse, prolonged intercourse without satisfaction.
- Infertility is the result of chronic inflammation of the spermatic cord, vesicles, testicles and their appendages.
- Cystitis, pyelonephritis (other diseases of the genitourinary system) are the result of hematogenous and mechanical spread of microorganisms.
- septicemia.
- Immunity continues to decline.
- Untreated prostatitis can lead to cancer in 35-40% of cases.
diagnosis
- Glandular rectal examination, aspiration of secretions for examination (culture to determine susceptibility to antibiotics).
- UAC, UAM, urine bacterial culture.
- STD smear test, upper gastrointestinal tract examination.
- The urinary rhythm is monitored daily and the urinary rate is measured (uroflowmetry).
- Perform ultrasound or TRUS for differential diagnosis.
- If tumor needs to be ruled out, a biopsy, urogram, and PSA (prostate-specific antigen) determination are performed.
- To diagnose infertility, a sperm test is performed - the analysis of semen to determine a man's fertility.

Treatment of acute prostatitis
- The most effective treatment for prostatitis is allotropic therapy. If the basis of prostatitis is infection, a course of antibacterial drugs is preferred to relieve the manifestations of inflammation.
- Pain syndromes can be relieved with analgesics, antispasmodics, rectal suppositories, microenemas containing warm analgesic solutions. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs may be used.
- Combinations of immunostimulants, immunomodulators, enzymes, vitamin complexes and trace elements have proven their effectiveness.
- Physiotherapy methods are possible only in the subacute stage of the disease. They improve microcirculation and increase immunity: UHF, microwave, electrophoresis, laser, magnetic therapy.
- Massage is another effective way to affect the prostate. It opens the ducts and normalizes blood circulation in the scrotum and pelvis.
- Acute renal filtrate retention can be corrected with catheterization and trocar cystostomy.
- The purulent process involves surgical intervention.
- Consultation with a psychologist.
Treatment of chronic prostatitis
- Herbal preparations are widely used in urological practice. They are able to accumulate at the sites of the most active pathological processes, protect cells from oxidation, scavenge free radicals and prevent glandular tissue proliferation.
- Antimicrobial treatment is selected individually based on the susceptibility of the microorganism to the drug.
- Immunity-boosting medications not only help deal with prostatitis but can also correct the negative effects of antibiotics that disrupt immune system function.
- Pain syndrome can be relieved by taking alpha-blockers and muscle relaxants.
- Prostate massage can mechanically remove "excess" secretions from the gland through the urethra, improve circulation, and minimize congestion.
- Physical therapy: laser, magnet, ultrasound, iontophoresis, warm sitz bath or herbal micro-enema.
- In severe cases, intravenous fluids containing diuretics may be needed. This stimulates the production of large amounts of urine, preventing the development of symptoms of intoxication, ascending cystitis, and pyelonephritis.
- For constipation, herbal laxatives can be used.
- Urologists and psychologists work with patients to develop a personal long-term plan that includes daily living, necessary rest, diet, moderate physical activity, and sexual activity.
- If the chronic process is resistant to treatment and the outflow of urine is blocked, surgical intervention is required: removal of all affected tissue (transurethral resection of the prostate) or complete removal of the gland and its surrounding tissue (prostatectomy). Practiced under special circumstances, it can lead to impotence and urinary incontinence. Young people do not undergo surgery because it can lead to infertility.
Symptoms and treatment of chronic prostatitis
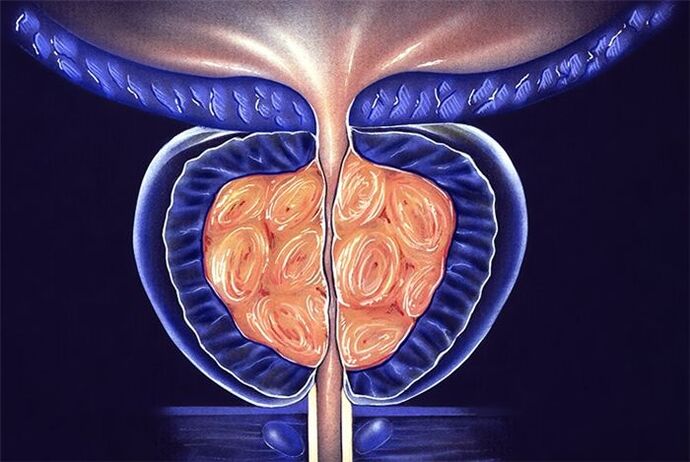
Causes of chronic prostatitis
- Coital rhythm disorder (irregular);
- Lack of physical activity, which is typical of overweight people;
- Being in a state of chronic stress;
- The predominance of fat-rich foods in the diet;
- Hazardous industries have negative effects on the body.
- Prostate surgery (if antimicrobial treatment was not performed before surgery);
- Refusal to use contraception;
- Lack of habit of keeping the body clean.
Symptoms of chronic prostatitis
laboratory research methods
- scraping from urethra;
- General and biochemical urinalysis;
- LHC cultures of prostate secretions.
Treatment of chronic prostatitis
- For men who are forced to sit most of the time (drivers, office workers, managers);
- For people who are overweight;
- For those who don't have time to exercise.
medical treatement
Treatment of bacterial chronic prostatitis
herbal treatment
- normalizes metabolism;
- Strengthen blood vessel walls;
- Activates blood circulation in the pelvic organs.
non-pharmacological treatment
- Activation of redox reactions;
- Improvement of blood microcirculation;
- New capillaries form;
- Pathogenic microbiota are suppressed;
- The process of cell division is activated, thereby promoting tissue regeneration.
Surgical treatment of chronic prostatitis
Exercise to treat chronic prostatitis
- Lie on a gymnastics mat with your arms extended upward.
- Bend your knees and pull them toward you while spreading them out in different directions.
- Elevate your pelvis as much as possible. Repeat 10-12 times.
- Lie on your stomach.
- Lift one leg, then the other. Repeat 10-12 times.